Γ函数
定义
Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma \,}函数可欧拉过欧拉(Euler)第二类积分定义:
对复数z{\displaystyle z\,},我们要求Re(z)>0{\displaystyle \mathrm {Re} (z)>0}。
Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma }函数还可以通过对e− − -->t{\displaystyle \mathrm {e} ^{-泰勒\,}做泰勒展开,解析延拓到整个复平面: Γ Γ -->(z)=∫ ∫ -->1∞ ∞ -->tz− − -->1etdt+∑ ∑ -->n=0∞ ∞ -->(− − -->1)nn!1n+z{\displaystyle \Gamma (z)=\int _{1}^{\infty }{\frac {t^{z-1}}{\mathrm {e} ^{t}}}{\rm {d}}t+\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {(-1)^{n}}{n!}}{\frac {1}{n+z}}}
这样定义的Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma }函数在全平面除了z=0,− − -->1,− − -->2,… … -->{\displaystyle z=0,-1,-2,\ldots }以外的地方解析。
Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma }函数也可以用无穷乘积的方式表示:
Γ Γ -->(z)=1z∏ ∏ -->n=1∞ ∞ -->(1+zn)− − -->1(1+1n)z{\displaystyle \Gamma (z)={\frac {1}{z}}\prod _{n=1}^{\infty }\left(1+{\frac {z}{n}}\right)^{-1}\left(1+{\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{z}}
这样定义的Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma }函数在全平面解析
无穷乘积
Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma \,}函数可以用无穷乘积表示:
其中γ γ -->{\displaystyle \gamma \,}是欧拉-马歇罗尼常数。
Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma }积分
⇒ ⇒ -->Γ Γ -->(α α -->)λ λ -->α α -->=∫ ∫ -->0∞ ∞ -->xα α -->− − -->1e− − -->λ λ -->xdx{\displaystyle \Rightarrow {\frac {\Gamma \left(\alpha \right)}{\lambda ^{\alpha }}}=\int _{0}^{\infty }x^{\alpha -1}\mathrm {e} ^{-\lambda x}{\rm {d}}x}
递推公式
Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma \,}函数的递推公式为: Γ Γ -->(x+1)=xΓ Γ -->(x){\displaystyle \Gamma (x+1)=x\Gamma (x)},
对于正整数n{\displaystyle n\,},有
Γ Γ -->(n+1)=n!{\displaystyle \Gamma (n+1)=n!},
可以说Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma \,}函数是阶乘的推广。
递推公式的推导
Γ Γ -->(n+1)=∫ ∫ -->0∞ ∞ -->e− − -->xxn+1− − -->1dx=∫ ∫ -->0∞ ∞ -->e− − -->xxndx{\displaystyle \Gamma (n+1)=\int _{0}^{\infty }\mathrm {e} ^{-x}x^{n+1-1}\mathrm {d} x=\int _{0}^{\infty }\mathrm {e} ^{-x}x^{n}{\rm {d}}x}
我们用分部积分法来计算这个积分:
∫ ∫ -->0∞ ∞ -->e− − -->xxndx=[− − -->xnex]0∞ ∞ -->+n∫ ∫ -->0∞ ∞ -->e− − -->xxn− − -->1dx{\displaystyle \int _{0}^{\infty }\mathrm {e} ^{-x}x^{n}\mathrm {d} x=\left[{\frac {-x^{n}}{\mathrm {e} ^{x}}}\right]_{0}^{\infty }+n\int _{0}^{\infty }\mathrm {e} ^{-x}x^{n-1}{\rm {d}}x}
当x=0{\displaystyle x=0\,}时,− − -->0ne0=01=0{\displaystyle {\tfrac {-0^{n}}{\mathrm {e} ^{0}}}={\tfrac {0}{1}}=0}。当x{\displaystyle x\,}趋于无穷大时洛必达法则达法则,有:
limx→ → -->∞ ∞ -->− − -->xnex=limx→ → -->∞ ∞ -->− − -->n!⋅ ⋅ -->0ex=0{\displaystyle \lim _{x\rightarrow \infty }{\frac {-x^{n}}{\mathrm {e} ^{x}}}=\lim _{x\rightarrow \infty }{\frac {-n!\cdot 0}{\mathrm {e} ^{x}}}=0}。
因此第一项[− − -->xnex]0∞ ∞ -->{\displaystyle \left[{\tfrac {-x^{n}}{\mathrm {e} ^{x}}}\right]_{0}^{\infty }}变成了零,所以:
Γ Γ -->(n+1)=n∫ ∫ -->0∞ ∞ -->xn− − -->1exdx{\displaystyle \Gamma (n+1)=n\int _{0}^{\infty }{\frac {x^{n-1}}{\mathrm {e} ^{x}}}{\rm {d}}x}
等式的右面正好是nΓ Γ -->(n){\displaystyle n\Gamma (n)\,}。因此,递推公式为:
重要性质

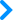
Γ函数在实轴上的函数图形
当z→ → -->0+{\displaystyle z\to 0^{+}}时,Γ Γ -->(z)→ → -->+∞ ∞ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma (z)\to +\infty }
欧拉反射公式:
乘法定理:
此外
此式可用来协助计算t分布概率密度函数、卡方分布概率密度函数、F分布概率密度函数等的累计概率。
极限性质
对任何实数α
特殊值
导数
对任何复数z,满足 Re(z) > 0,有
于是,对任何正整数 m
其中 γ 是欧拉-马歇罗尼常数。
复数值
斯特灵公式
斯特灵公式能用以估计Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma }函数的增长速度。
解析延拓
Γ函数的绝对值函数图形
注意到在Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma }函数的积分定义中若取z{\displaystyle z\,}为实部大于零之复数、则积分存在,而且在右半复平面上定义一个全纯函数。利用函数方程
并注意到函数sin -->(π π -->z){\displaystyle \sin(\pi z)\,}在整个复平面上有解析延拓,我们可以在Re(z)<1{\displaystyle \mathrm {Re} (z)<1}时设
从而将Γ Γ -->{\displaystyle \Gamma \,}函数延拓为整个复平面上的亚纯函数,它在z=0,− − -->1,− − -->2,− − -->3⋯ ⋯ -->{\displaystyle z=0,-1,-2,-3\cdots }有单极点,留数为
参见
双伽玛函数
多伽玛函数
如何利用EXCEL求伽玛函数的值
利用EXCEL中的GAMMALN函数,再用EXP[GAMMALN(X)],即可求得任意数的伽玛函数的值。
举例:EXP[GAMMALN(4/3)]=0.89298
免责声明:以上内容版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。感谢每一位辛勤著写的作者,感谢每一位的分享。

- 有价值
- 一般般
- 没价值







推荐阅读


关于我们

APP下载