化学疗法
医疗机制
由于癌细胞的增殖比正常细胞快,抗癌药物的作用原理通常是阻断细胞分裂以抑制癌细胞生长,如一些药物可以抑制脱氧核糖核酸进行复制。化疗药物一般也同时杀死正常细胞,因而伤害了需要进行分裂以维持正常功能的健康组织,例如毛发基部细胞和肠粘膜细胞,使病人常伴有脱发及恶心呕吐等症状。一般情况下,化疗药物是毒性强的先打,时间短的先打,化疗药物换的时候一般用生理盐水冲洗,以减少药物过敏。例如长春瑞滨毒性较强,一般先打,打之前推地塞米松抗过敏,打的时候速度要快,使其尽快通过血管;多西他赛这种药物乃是紫杉醇的衍生物,这种药物毒性小,效果好,打的时候要给病人上心电监护,随时观察。不过在打格拉司琼的时候后面可以直接打化疗药物。如果发生化疗药物外渗,则立即停止注入,尽快吸收针头内的残留液体,拔出针头,局部冷敷湿敷,用硫酸镁溶液局部湿敷,并抬高患肢24小时。
当然,也有用于非肿瘤治疗,如指抗生素(抗菌化疗)。从这个意义上讲,首先应用化疗剂的是保罗·埃利希,他于1909年用含砷化合物治疗梅毒。其他化学疗法的用法可以是用于治疗自身免疫性疾病,如多发性硬化症、类风湿性关节炎和抑制后的排斥反应等。
图片
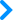
西德尼·法伯,现代化疗之父
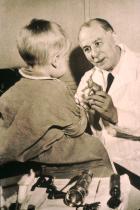
六种化疗药物,从中间顺时针数分别是博来霉素、长春新碱、达卡巴嗪、环磷酰胺、阿霉素、依托泊苷
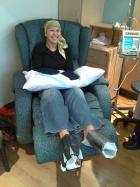
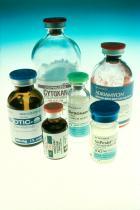
一位女性乳癌病患正在接受欧洲紫杉醇化疗。手脚各别套上冷手套(手)及 酒类冷却装置 ( 英语 : Wine accessory#Wine coolers ) (脚)以减低对指甲的伤害。
治疗策略
There are a number of strategies in the administration of chemotherapeutic drugs used today. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative ( 英语 : cure ) intent or it may aim to prolong life or topalliate symptoms.
Induction chemotherapy is the first line treatment of cancer with a chemotherapeutic drug. This type of chemotherapy is used for curative intent.
Combined modality chemotherapy is the use of drugs with othercancer treatments, such assurgery,radiation therapy, and/or hyperthermia therapy ( 英语 : hyperthermia therapy ) .
Consolidation chemotherapy is given after remission in order to prolong the overall disease-free time and improve overall survival. The drug that is administered is the same as the drug that achieved remission.
Intensification chemotherapy is identical to consolidation chemotherapy but a different drug than the induction chemotherapy is used.
Combination chemotherapy ( 英语 : Combination chemotherapy ) involves treating a patient with a number of different drugs simultaneously. The drugs differ in their mechanism and side-effects. The biggest advantage is minimising the chances of resistance developing to any one agent. Also, the drugs can often be used at lower doses, reducing toxicity.
Neoadjuvant ( 英语 : Neoadjuvant ) chemotherapy is given prior to a local treatment such as surgery, and is designed to shrink the primary tumor. It is also given to cancers with a high risk of micrometastatic disease.
Adjuvant chemotherapy ( 英语 : Adjuvant chemotherapy ) is given after a local treatment (radiotherapy or surgery). It can be used when there is little evidence of cancer present, but there is risk of recurrence. It is also useful in killing any cancerous cells that have spread to other parts of the body. These micrometastases ( 英语 : micrometastases ) can be treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and can reduce relapse rates caused by these disseminated cells.
Maintenance chemotherapy is a repeated low-dose treatment to prolong remission.
Salvage chemotherapy or palliative chemotherapy is given without curative intent, but simply to decrease tumor load and increase life expectancy. For these regimens, in general, a better toxicity profile is expected.
All chemotherapy regimen ( 英语 : chemotherapy regimen ) s require that the patient be capable of undergoing the treatment. Performance status ( 英语 : Performance status ) is often used as a measure to determine whether a patient can receive chemotherapy, or whether dose reduction is required. Because only a fraction of the cells in a tumor die with each treatment ( fractional kill ( 英语 : fractional kill ) ), repeated doses must be administered to continue to reduce the size of the tumor. Current chemotherapy regimens apply drug treatment in cycles, with the frequency and duration of treatments limited by toxicity to the patient.
参见
不良反应 (医学)
病人安全
标靶药物
放射线治疗
太平洋紫杉醇
西德尼·法伯 ( 英语 : Sidney Farber )
达卡巴嗪 ( 英语 : Dacarbazine )
免责声明:以上内容版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。感谢每一位辛勤著写的作者,感谢每一位的分享。

- 有价值
- 一般般
- 没价值







推荐阅读


关于我们

APP下载